Molecules drawing atoms chemistry molecule draw simple lego science danielyeow diagram water atom most particles store lms betterlesson convenience matter
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling to draw molecules? Do you want to create accurate and beautiful molecular diagrams? If so, you have come to the right place! In this article, we will teach you how to draw a molecule step-by-step, using easy and effective methods that anyone can follow. Whether you are a student, researcher, or science enthusiast, learning how to draw a molecule is key to understanding the world of chemistry.
Drawing a molecule can be challenging, especially for beginners. It requires knowledge of chemistry concepts, such as valence electrons, bonding, and molecular geometry, as well as artistic skills, such as proportion, shading, and labeling. Many people struggle with drawing molecules because they do not know where to start, how to choose the right perspective, or how to represent the 3D structure on a 2D plane. Others may find it difficult to keep track of the atoms, bonds, and functional groups, or to distinguish between isomers and stereoisomers. However, with some practice and guidance, anyone can master the art of drawing molecules.
To draw a molecule, you need to follow four main steps: choose a molecule, determine its structure, sketch its skeleton, and add details. Firstly, choose a molecule that you want to draw, such as water, ammonia, or glucose. Secondly, determine the structure of the molecule, including the number and type of atoms, the type of bonds, and the shape of the molecule. You can use software programs, such as ChemDraw, MarvinSketch, or Avogadro, to visualize and manipulate the molecule in 3D. Thirdly, sketch the skeleton of the molecule, using simple geometric shapes, such as circles, triangles, and lines. This will help you to position the atoms and bonds accurately and proportionally. Lastly, add details to the molecule, such as lone pairs, charges, and functional groups, and label the atoms and bonds with their names and symbols.
In summary, drawing a molecule requires four main steps: choose, determine, sketch, and add. By following these steps and practicing regularly, you can improve your ability to draw molecules and enhance your understanding of chemistry concepts. Moreover, drawing molecules can be a fun and rewarding activity that boosts your creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills.
How to draw a molecule: Water
Let’s start with a simple molecule, water (H2O), which consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Water is a vital compound for life and has many interesting properties, such as polarity, hydrogen bonding, and surface tension. Drawing water molecule can be a good starting point for learning how to draw molecules.
First, take a clean sheet of paper and a pencil. Draw a small circle in the center of the paper, representing the oxygen atom. Then, draw two small circles on either side of the oxygen circle, representing the hydrogen atoms. Connect the hydrogen circles to the oxygen circle with short lines, representing the covalent bonds. The angle between the bonds should be about 105 degrees, forming a bent or V-shaped molecule. Add two dots above the oxygen circle, representing the two lone pairs of electrons. Label the atoms and bonds with their symbols and names, such as H and O. Finally, shade the water molecule to give it a 3D appearance, using light and dark tones to show the relative positions of the atoms and bonds.
 How to draw a molecule: Ammonia
How to draw a molecule: Ammonia
Another example of a simple molecule is ammonia (NH3), which consists of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms. Ammonia is a common compound in many industrial and biological processes, such as the Haber-Bosch process and nitrogen fixation. Drawing ammonia molecule can help you to understand the basics of molecular geometry and hybridization.
First, draw a small circle in the center of the paper, representing the nitrogen atom. Then, draw three small circles around the nitrogen circle, representing the hydrogen atoms. Connect the hydrogen circles to the nitrogen circle with short lines, representing the covalent bonds. The angle between the bonds should be about 107 degrees, forming a trigonal pyramidal or VSEPR shape. Add one dash above the nitrogen circle, representing the lone pair of electrons. Label the atoms and bonds with their symbols and names, such as H and N. Finally, shade the ammonia molecule to give it a 3D appearance, using light and dark tones to show the relative positions of the atoms and bonds.
 ### Hybrid orbitals and molecular geometry
### Hybrid orbitals and molecular geometry
In chemistry, hybridization is the process of combining atomic orbitals to form hybrid orbitals that are suitable for bonding. The type and number of hybrid orbitals depend on the geometry and number of bonds in the molecule. For example, water molecule has a tetrahedral electron arrangement but a bent molecular shape, which can be explained by the sp3 hybrid orbitals of the oxygen atom. Similarly, ammonia molecule has a trigonal pyramidal electron arrangement but a distorted tetrahedral molecular shape, which can be explained by the sp3 hybrid orbitals of the nitrogen atom.
Bonding and resonance structures
Bonding is the attraction between atoms that holds them together in a molecule. There are three main types of bonds: covalent, ionic, and metallic. Covalent bond is the sharing of electrons between two or more atoms, while ionic bond is the transfer of electrons between two oppositely charged ions. Metallic bond is the sharing of a sea of electrons between many atoms in a metal. In addition, some molecules can have resonance structures, which are multiple Lewis structures that contribute to the overall shape and stability of the molecule.
Question and Answer
Q: What is the difference between a Lewis structure and a molecular shape?
A: A Lewis structure is a diagram that shows the arrangement of atoms and electrons in a molecule, whereas a molecular shape is a 3D arrangement of atoms in a molecule that is determined by the electron and bond geometry. A Lewis structure can give you information about the bonding and lone pairs in the molecule, while a molecular shape can give you information about the polarity, reactivity, and physical properties of the molecule.
Q: How can I determine the hybridization of an atom in a molecule?
A: To determine the hybridization of an atom, you need to count the number of electron domains (bonding and nonbonding pairs of electrons) around the atom, and then match that number with the appropriate hybridization scheme, such as sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, or sp3d2. For example, if an atom has four electron domains (including one double bond), its hybridization is sp3. If an atom has two electron domains (both double bonds), its hybridization is sp.
Q: How can I tell if a molecule is polar or nonpolar?
A: To determine the polarity of a molecule, you need to look at the electronegativity difference between the atoms and the geometry of the molecule. If the difference in electronegativity is greater than 0.4, the bond is polar covalent, and the molecule may be polar or nonpolar, depending on the shape of the molecule. For example, water molecule is polar because it has a bent molecular shape and a net dipole moment, while carbon dioxide molecule is nonpolar because it has a linear molecular shape and no net dipole moment.
Q: How can I draw a resonance structure of a molecule?
A: To draw a resonance structure of a molecule, you need to identify the atom that has a double bond or a lone pair of electrons, and then move the electrons to the adjacent atom(s) to form a new bond or a lone pair of electrons. You can draw as many resonance structures as needed to show the delocalization of electrons in the molecule, while maintaining the same bond order and formal charge on each atom. For example, the carbonate ion (CO32-) has three resonance structures that contribute to its stability and reactivity.
Conclusion of how to draw a molecule
In conclusion, drawing a molecule is an essential skill for anyone who wants to understand and communicate chemistry concepts. By following the four main steps of choosing, determining, sketching, and adding, you can create accurate and beautiful molecular diagrams that showcase your creativity and knowledge. Whether you are a student who is studying for an exam, a researcher who is presenting a poster, or a science enthusiast who is sharing a blog post, learning how to draw a molecule can make your work more effective, engaging, and memorable.
Gallery
32 Draw And Label A Water Molecule - Labels 2021
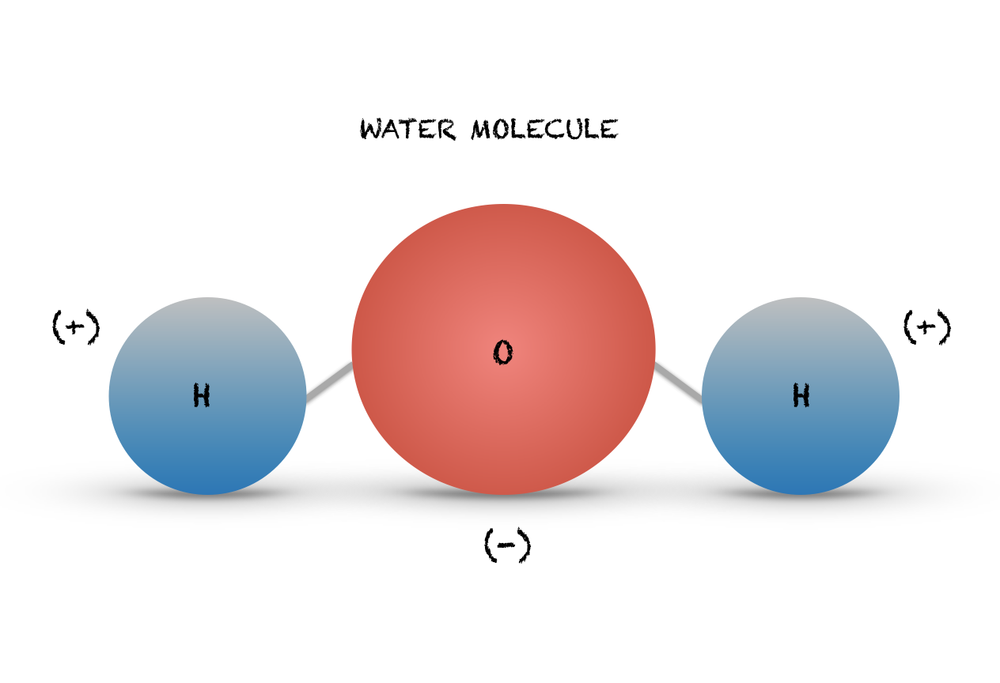
Photo Credit by: bing.com / molecule atoms partial
Drawing Molecules | Danielyeow.com
Photo Credit by: bing.com / molecules drawing atoms chemistry molecule draw simple lego science danielyeow diagram water atom most particles store lms betterlesson convenience matter
Chemistry Drawing Free At GetDrawings | Free Download
Photo Credit by: bing.com / chemistry molecule drawing organic molecules chemical structure science line model drawings illustrations getdrawings vector background clip icon
Drawing Molecules | Danielyeow.com

Photo Credit by: bing.com / molecules drawing molecule 3d danielyeow atoms 3o2
Drawing 3D Molecules - YouTube

Photo Credit by: bing.com / drawing molecule molecules 3d paintingvalley





